
 |
Accelerator |
A machine that is used to speed up particles. Particle physicists can use accelerators to smash particles into each other to study what they are made of. |
Annihilation |
|
What happens when matter is converted into energy. An example is when a proton and antiproton collide and they are gone, but energy remains in their place. |
Antimatter |
|
Matter is the stuff that everything is made of. Antimatter is the its counterpart. The antimatter particle will have the same mass as its matter counterpart, but all the other properties are opposite. For example, the positron is the antimatter counterpart (or antiparticle) of the electron. It has the same mass as the electron, but has positive electric charge instead of negative electric charge. |
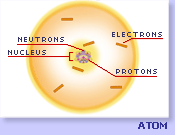 |
Atom |
A very small (microscopic) structure found in all matter around us that has all of the chemical properties of an element. An atom has electrons and a nucleus that contains protons and neutrons. click to enlarge image. |
